Cervical Cancer: Prevent with Screening and HPV Vaccination
Center : Women Health Center
Article by : Dr. Jutaporn Uthaisan

Cervical cancer is the second most common cancer among women, following breast cancer. Each year, this type of cancer affects around 10,000 Thai women. The primary cause of this cancer is infection with the Human Papillomavirus (HPV), a virus that spreads easily through direct contact or sexual intercourse. There are over 100 types of HPV, but types 16 and 18 are responsible for about 70% of cervical cancer cases in women. However, cervical cancer can be prevented if detected early. HPV vaccination also significantly reduces the risk of developing cervical cancer.
Table of Contents
- What is Cervical Cancer?
- Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
- Risk Factors and Groups at Risk for Cervical Cancer
- Stages of Cervical Cancer
- Cervical Cancer Diagnosis
- Cervical Cancer Treatment Methods
- Prevention of Cervical Cancer
- Cervical Cancer Can Be Treated if Detected Early at Nakornthon Hospital
- Free Online Consultation with a Specialist
What is Cervical Cancer?
Cervical cancer occurs when abnormal cells in the cervix grow uncontrollably and may spread to nearby organs or other parts of the body. The leading cause is HPV (Human Papillomavirus) infection, especially high-risk strains such as types 16 and 18. In its early stages, cervical cancer usually does not show any signs or symptoms, making early detection through screening and HPV vaccination essential for all women. Early detection increases the chances of successful cervical cancer treatment.
Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
What causes cervical cancer? HPV infection is the primary cause, and it often presents no symptoms until the disease becomes more advanced. If any abnormal signs appear, it is important to see a doctor for immediate evaluation. Signs of cervical cancer include:
- Irregular menstrual periods
- Bleeding between menstrual cycles
- Unusual vaginal bleeding after intercourse (that has not occurred before)
- Vaginal discharge with blood or pus /
- Foul-smelling vaginal odor
Risk Factors and Groups at Risk for Cervical Cancer


The main cause of cervical cancer is infection with high-risk HPV strains, usually transmitted through sexual activity. Additional risk factors that may increase the chance of developing cervical cancer include:
- Early onset of sexual activity
- Multiple or frequently changing sexual partners
- History of sexually transmitted infections such as syphilis, gonorrhea, or herpes
- Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV
- Women who smoke have a higher risk of cervical cancer
Stages of Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is classified into stages based on how far it has spread, which is crucial for treatment planning and prognosis. The four main stages are:
- Stage 1: Cancer cells are limited to the cervix
- Stage 2: Cancer has spread outside the cervix but not to the pelvic wall or lower third of the vagina
- Stage 3: Cancer has spread to the pelvic wall, lower third of the vagina, or caused kidney swelling due to ureter blockage
- Stage 4: Advanced stage where cancer spreads to distant organs such as the bladder, rectum, lungs, liver, lymph nodes, bones, or other parts of the body

Cervical Cancer Diagnosis
Initial cervical cancer screening involves the Pap test combined with HPV DNA testing. If abnormal cells or high-risk HPV strains are detected, the doctor may recommend further diagnostic procedures, including:
Colposcopy: A detailed examination of the cervix and vagina using a special magnifying device to identify abnormal areas not visible to the naked eye. A chemical solution is applied to highlight abnormal cells, and suspicious tissue is biopsied for further analysis.
Cervical Cancer Treatment Methods
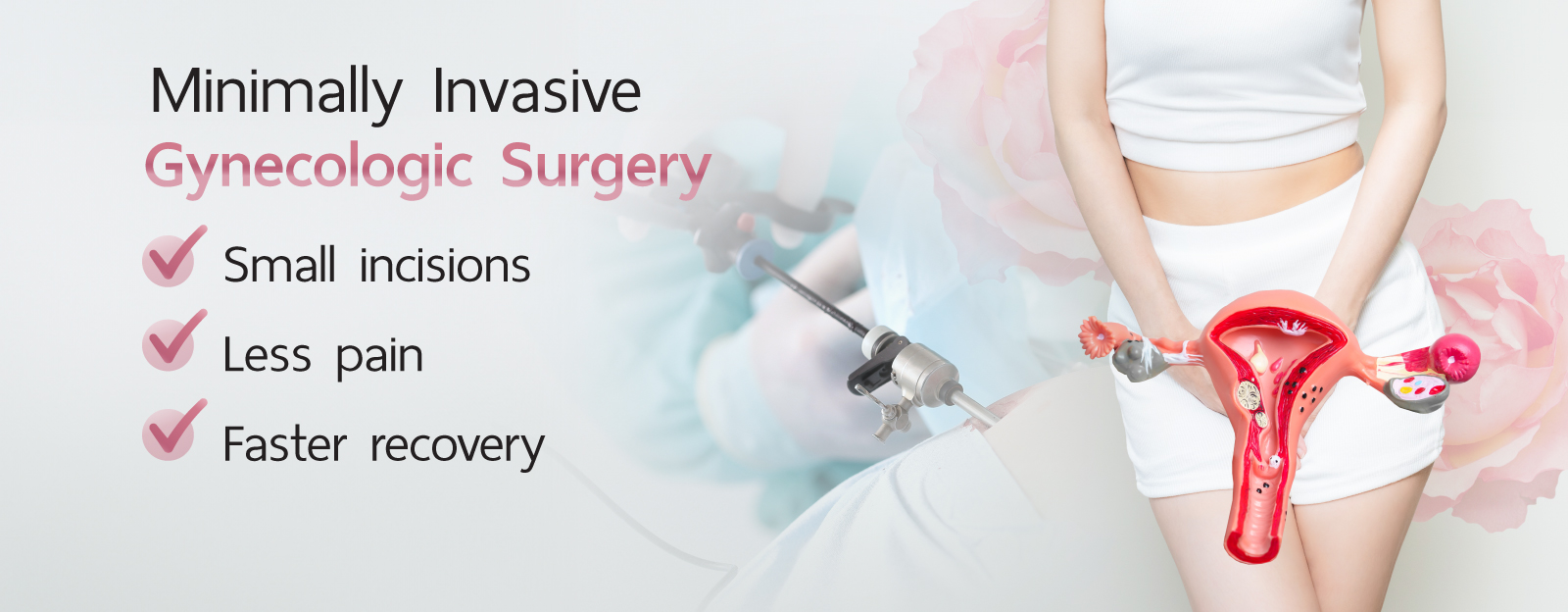

Cervical cancer treatment depends on the stage of the disease and includes:
Surgery
Surgical options are often used for early-stage cervical cancer and may include:
- Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure (LEEP)
- Trachelectomy (removal of part of the cervix)
- Hysterectomy (removal of the uterus)
- Radical hysterectomy (removal of the uterus along with surrounding tissue), based on disease stage and patient age
Radiation Therapy and Chemotherapy
This approach uses radiation, often combined with chemotherapy, to kill cancer cells.
Targeted medicines and immunotherapy
Targeted therapy uses drugs designed to attack cancer cells specifically. Immunotherapy boosts the body's immune system to fight cancer more effectively.
Palliative Treatment for Cervical Cancer
Palliative care focuses on symptom relief and improving quality of life rather than curing the disease. It supports the patient’s physical and emotional well-being throughout the illness.
Prevention of Cervical Cancer

Cervical cancer can be effectively prevented through methods aimed at reducing HPV infection risk and early detection of abnormal cervical cells:
- HPV Vaccination: Highly effective in preventing HPV infection, the main cause of cervical cancer. Recommended from age 9.
- Cervical cancer screening: Helps detect precancerous changes early. Women should begin cervical cancer screening at age 25 using:
- Pap Test: Collects cervical cells to check for abnormalities
- HPV DNA Test: Detects HPV at the molecular level before cancer develops
- Avoid Risky Behaviors: Delaying sexual activity, limiting the number of sexual partners, and consistently using condoms can reduce the risk of HPV and other STIs
- Healthy Lifestyle: Eating nutritious food, regular exercise, and adequate rest strengthen the immune system to fight off HPV
- Quitting Smoking: Reduces the risk of cervical cancer
Cervical Cancer Can Be Treated if Detected Early at Nakornthon Hospital
Cervical cancer is often a silent threat with no early signs. If you experience any symptoms of cervical cancer, consult a doctor immediately for proper screening and diagnosis. The Women Health Center at Nakornthon Hospital provides comprehensive care for women of all ages, including cervical cancer screening and diagnosis by specialists. Using modern technology, we offer safe and effective treatment for gynecologic cancers such as cervical and ovarian cancer, ensuring the best possible care with compassion and understanding.
For more information, please contact:
- - Website : https://en.nakornthon.com
- - Facebook : Nakornthon Hospital - International Patient
- - Line : @nakornthoninter
- - Tel: 02-450-9999 (Available 24 hours)
Free Online Consultation
Article of Women Health Center